
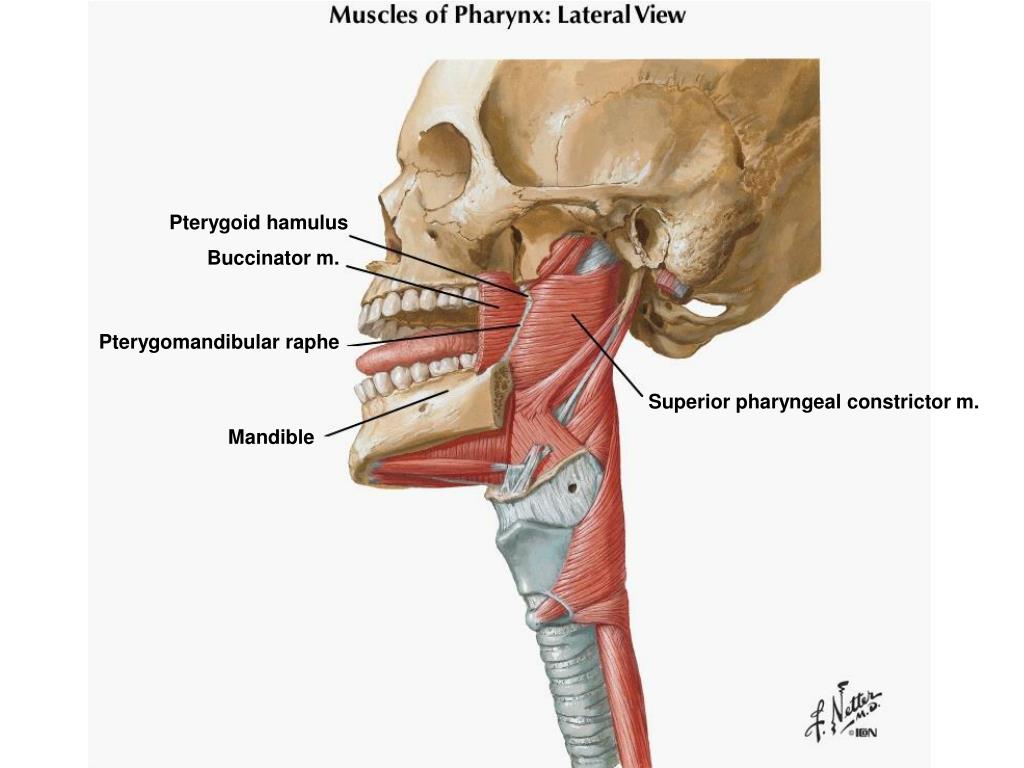
Because it is also a tongue muscle it is often grouped with them also but here to lessen redundancy we will assume you will remember that and we will not cover it again. This is important to help force food into the pharynx. This muscle acts to lift the tongue towards the palate while simultaneously lowering the soft palate towards the tongue. As they run from their origin in the palatine aponeurosis to the insertion in the tongue it forms a curtain of tissue which as a continuation from the posterior border of the soft palate defines the posterior extent of the oral cavity. The palatoglossus muscles form the anterior tonsillar pillars which lie anterior to the palatine tonsils so are easily visualized by looking in a properly illuminated throat.

It, like the levator veli palatini, is innervated by fibers from the vagus nerve. It will elevate the thyroid cartilage when contracted which by extension raises the larynx and pharynx. They are formed as the muscle goes from its origin in the palatal aponeurosis and adjacent hard palate and its insertion in the thyroid cartilage.

These bilateral structures are referred to as the posterior tonsillar pillars. The left and right palatopharygeus muscles actually underlie a structure you can see in your own mouth, if your palatine tonsils are either missing or small enough, as it lies directly behind the palatine tonsil on both sides of the mouth. It is innervated by nerves that originate in the vagus nerve (cranial nerve X). When contracted it helps open the eustachian tube but as indicated by its name it elevates the palate also. Its insertion is on the palatine aponeurosis. It originates on the petrous portion of the temporal bone and like the tensor veli palatini also from the eustachian tube though on the medial side rather than the lateral side.
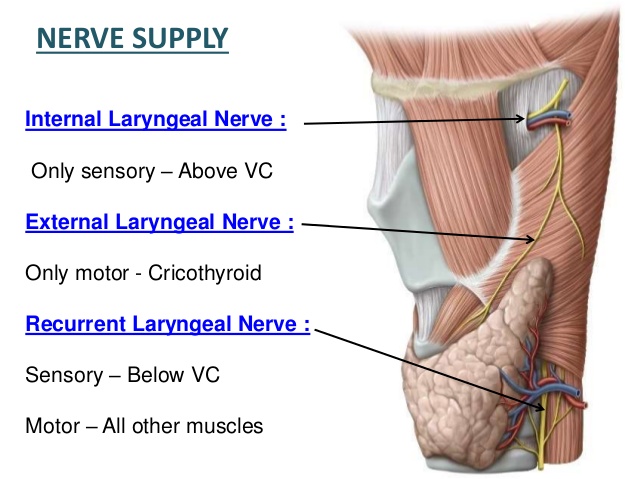
It is the only palatal muscle not innervated by the vagus (cranial nerve X).Īnother small paired muscle found in the soft palate is the levator veli palatini. It is innervated by a branch of the nerve to the medial pterygoid which one should remember is a muscle of mastication and therefore originates from the third division of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V3 – cranial nerve V - 3rd division). It is activated when swallowing which is why swallowing helps relieve the pressure buildup in the ear when changing altitude especially noticeable when flying. When contracted it has two effects: it tenses the palatal aponeurosis which anchors other muscles, so it acts as a synergist to their actions and importantly also helps open the eustachian tube to equalize the pressure in the middle ear. It inserts on a band of connective tissue that runs along the posterior edge of the hard palate. This paired muscle, the tensor veli palatini originates over an area that includes the medial pterygoid plate of the sphenoid, the spine of the sphenoid and importantly on the lateral surface of the cartilage that forms the eustachian (auditory) tube.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
